Development Environment
Introduction
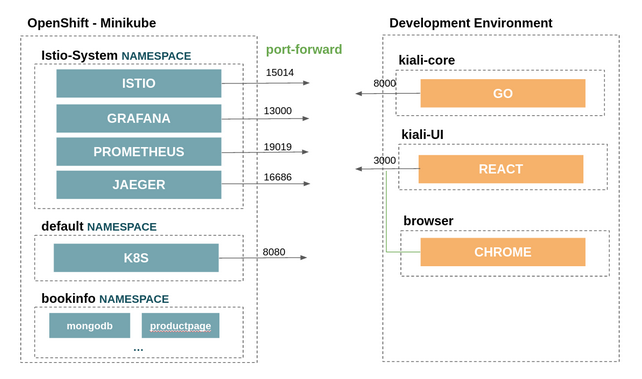
In this section it is explained how to set up a development environment:
- As described in Architecture, we would need to have the Kiali dependencies running in an OpenShift or Kubernetes
- We will use a port forward to access those services outside the cluster.
- We will have the project source running locally. In this case we will set up an IDE.
- Bookinfo application example will also be running on our cluster.
Prerequisites
- Development tools are installed:
- Kiali source code: We will fork the 3 kiali repositories, and then, clone them in a local folder:
- Istio and the required services are running in Minikube or OpenShift. To install it following the above schema, it is possible to use the following scripts (From the Kiali repository):
hack/istio/install-istio-via-istioctl.sh: Installs the latest Istio release into istio-system namespace along with the Prometheus, Grafana, and Jaeger addons.hack/istio/install-bookinfo-demo.sh: Installs the Bookinfo demo that is found in the Istio release that was installed via the hack/istio/install-istio-via-istioctl.sh hack script.- Pass in
-tgto also install a traffic generator that will send messages periodically into the Bookinfo demo. - If using Minikube and the
-tgoption, make sure you pass in the Minikube profile name via-mpif the profile name is notminikube.
- Pass in
Port forward
Before the setup, we will need to do a port-forward of the services that kiali is using.
We can use the hack/run-kiali.sh script for this purpose. It can work without any options. Pass –help to see the options it takes.
An example to run it following the above schema:
./run-kiali.sh -pg 13000:3000 -pp 19090:9090 -app 8080 -es false -iu http://127.0.0.1:15014
Local Configuration File
The go process will require a configuration to point to these services and other specific configurations. This file will be places in ~/kiali/config.yaml, and referenced later by the GO local process.
api:
namespaces:
exclude:
- istio-operator
- kube.*
- openshift.*
- ibm.*
- kiali-operator
label_selector: ""
server:
address: localhost
port: 8000
static_content_root_directory: /home/userTests/kiali-static-files
in_cluster: false
deployment:
accessible_namespaces: [ "**" ]
extensions:
iter_8:
enabled: true
external_services:
istio:
istio_canary_revision:
current: prod
upgrade: canary
url_service_version: http://localhost:15014/version
config_map_name: istio
istio_identity_domain: svc.cluster.local
prometheus:
url: http://localhost:19090
cache_enabled: true
tracing:
enabled: true
internal_url: http://localhost:16685/jaeger
external_url: http://localhost:16686/jaeger
use_grpc: false
whitelist_istio_system:
- jaeger-query
- istio-ingressgateway
namespace: istio-system
port: 443
service: tracing
auth:
insecure_skip_verify: false
password: cTSM/77tNZ0yGw/ZJXkO7IObbemLJjFkCp4GuqLzXIgE8RWrJvWjFViv9Dpu0SguxD3N/oCUPJnyreoHuSCNZ9kFTrHgRl033waUpTAYZPCEzMPw9Rui5C3/o5x4bclHq0IQ8OGr5LuN2L1WCXrEo9iUntPMovbsP1Alqwh0LZ79ztIkObNBNniX1tuo0fM9O53QKSAjGBnK13LFjHC7wXo+mWw1fzHf9x4jib6UDbeuzHfugDS0Mtj4E9QDRHjpPUrh66dVib4kCJ4nMO19BuiIk+OgbNdhBhg3wn1fn7F6+d/i6Mbq/C/OJylSL6ewUVwIvIAmcRM/jdTqdz0w
type: basic
use_kiali_token: false
username: internal
grafana:
internal_url: http://localhost:13000
external_url: http://localhost:13000
dashboards:
- name: "Istio Service Dashboard"
variables:
namespace: "var-namespace"
service: "var-service"
- name: "Istio Workload Dashboard"
variables:
namespace: "var-namespace"
workload: "var-workload"
custom_dashboards:
enabled: false
#health_config:
# rate:
# - namespace: "alpha"
# tolerance:
# - code: "4XX"
# degraded: 30
# failure: 50
# protocol: "http"
# - code: "5XX"
# degraded: 30
# failure: 50
# protocol: "http"
# - namespace: "beta"
# tolerance:
# - code: "[4]\\d\\d"
# degraded: 30
# failure: 40
# protocol: "http"
# - code: "[5]\\d\\d"
# protocol: "http"
auth:
strategy: anonymous
login_token:
signing_key: test
kubernetes_config:
cache_enabled: true
cache_duration: 300
cache_namespaces:
- bookinfo
- istio-system
cache_token_namespace_duration: 120
excluded_workloads: []
kiali_feature_flags:
istio_injection_action: true
istio_upgrade_action: false
istio_labels:
app_label_name: app
injection_label_name: istio-injection
injection_label_rev: istio.io/rev
version_label_name: version
Local Processes
In this section we will start the 3 local processes for kiali:
- kiali-core: The backend Go process
- kiali-ui: The frontend React process
- browser: The Javascript debugger process.
In this example, we will create the configurations in the Jetbrains Golang IDE.
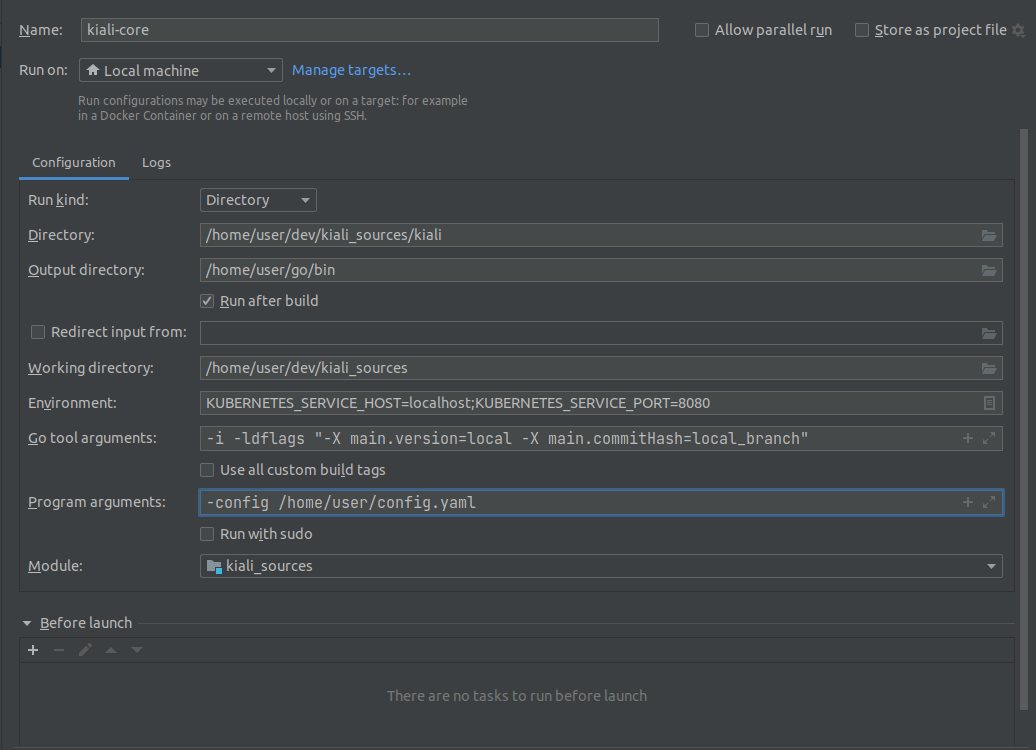
kiali-core
To run the Kiali backend.
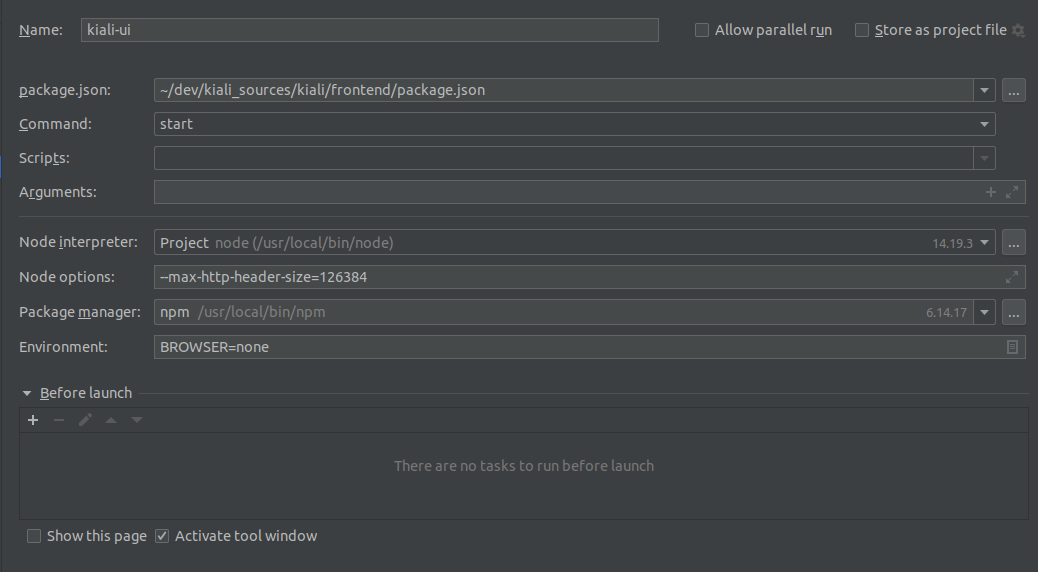
kiali-ui
In order to forward the requests to the backend propertly, we will need to add the following line in kiali/frontend/package.json:
"proxy": "http://localhost:8000",
browser
This process is required to debug the frontend.
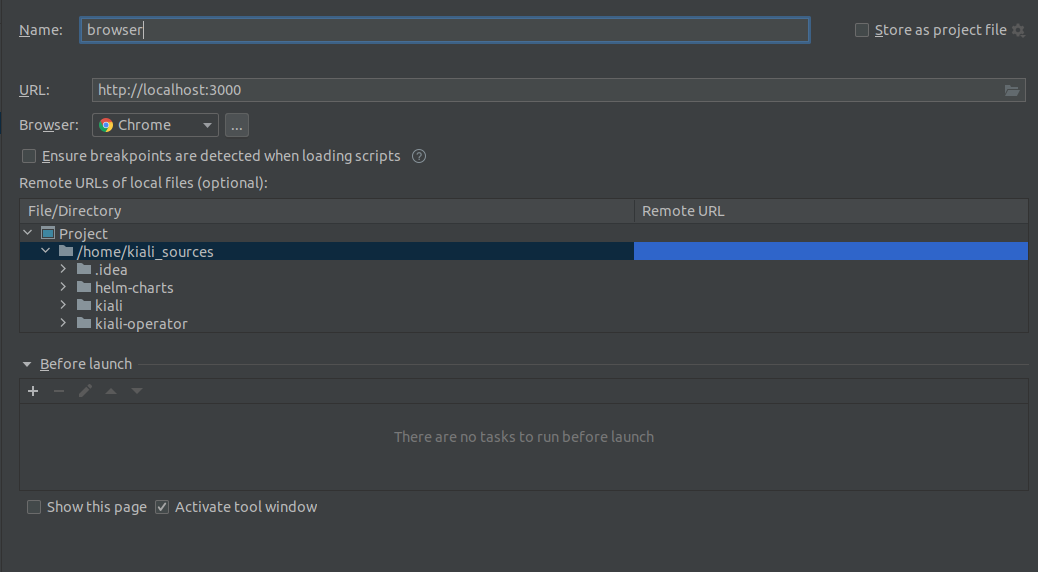
After running the 3 processes, we should be able to access Kiali GUI in localhost:3000
Using VisualStudio Code
To run kiali in a debugger, a file “launch.json” should be created in your local kiali local repo’s .vscode directory (e.g. home/source/kiali/kiali/.vscode/launch.json). The file should look like:
{
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Launch Kiali to use hack script services",
"type": "go",
"request": "launch",
"mode": "debug",
"program": "${workspaceRoot}/kiali.go",
"cwd": "${env:HOME}/tmp/run-kiali",
"args": ["-config", "${env:HOME}/tmp/run-kiali/run-kiali-config.yaml"],
"env": {
"KUBERNETES_SERVICE_HOST": "127.0.0.1",
"KUBERNETES_SERVICE_PORT": "8001",
"LOG_LEVEL": "trace"
}
}
]
}
run-kiali.sh should be started like this:
hack/run-kiali.sh --tmp-root-dir $HOME/tmp --enable-server false